近期,实验室博士生付金宇作为第一作者、实验室孙光辉教授作为通讯作者的论文“On Trajectory Homotopy to Explore and Penetrate Dynamically of Multi-UAV”被国际权威期刊IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems录用。
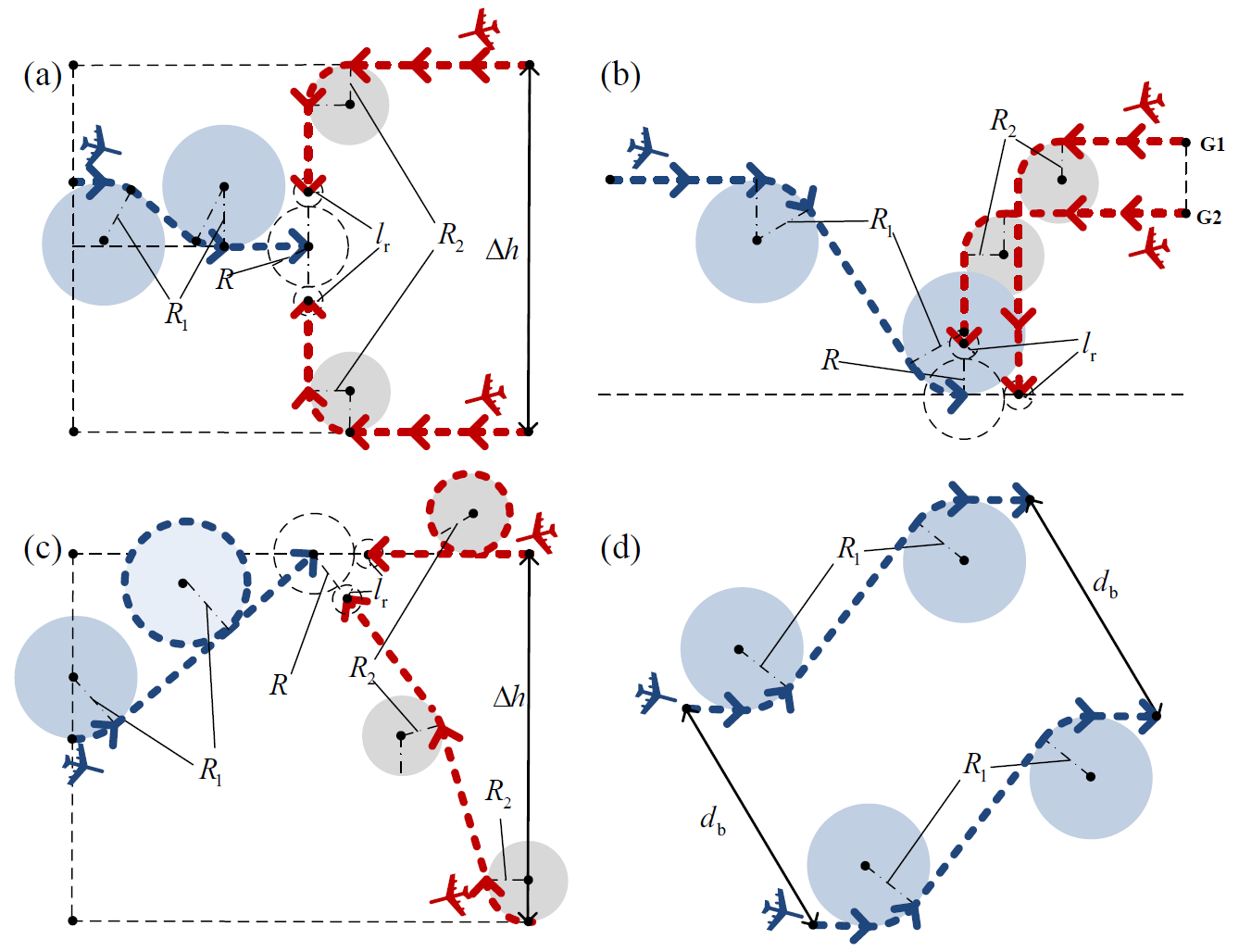
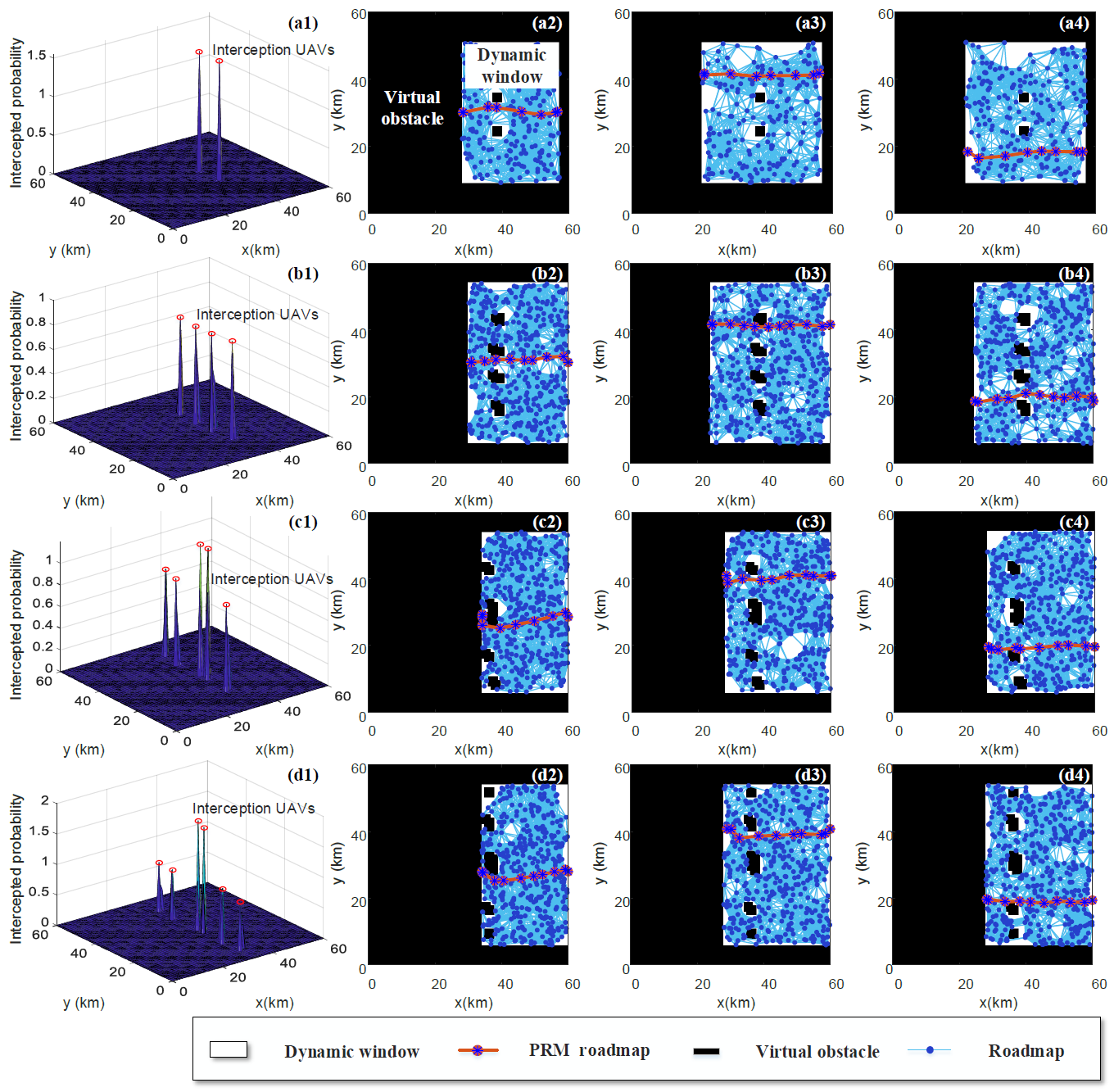
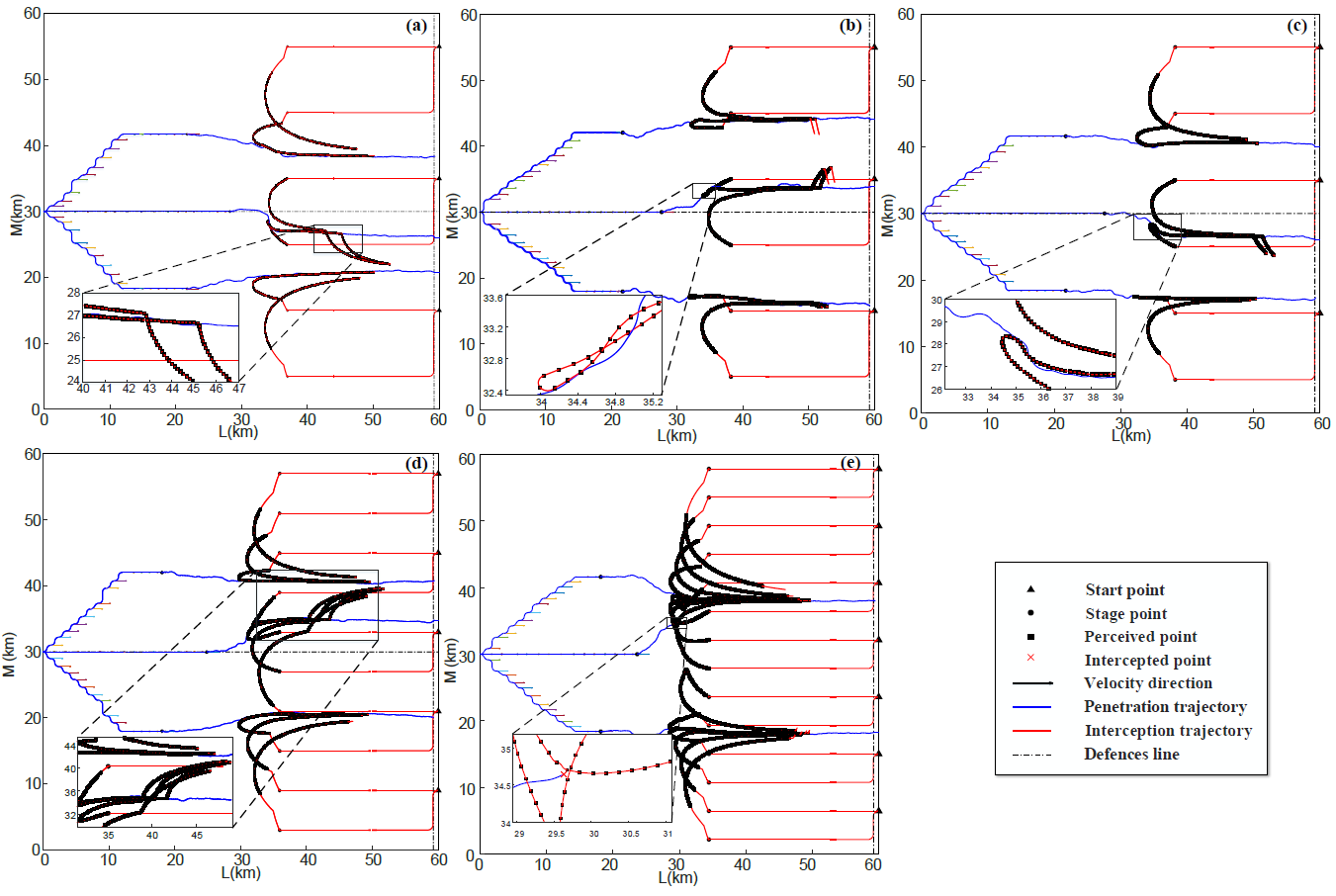
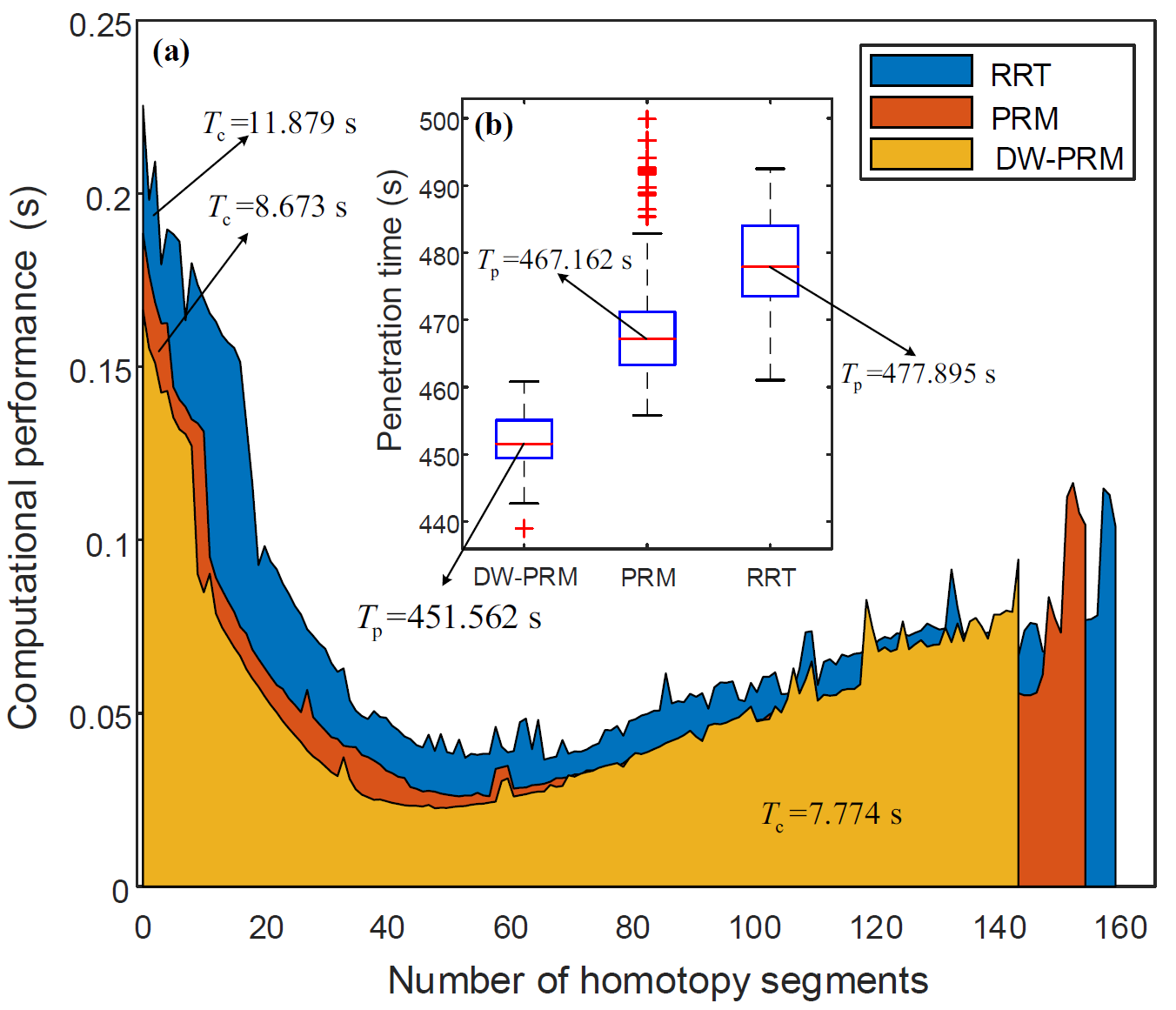
论文针对多无人机突防任务规划 (penetration mission Planning, PMP),研究了一种轨迹同伦优化框架,解决了“敌对障碍”及感知受限环境下的动态突防任务规划问题。充分考虑突防过程的实际约束,为提高突防路径求解的效率,构造了一种新的时变机制,以适应未知目标搜索(UTS)和动态轨迹规划(DTP)两个阶段的延迟时间更新。利用高斯概率场(GPF)建立占据栅格地图,用于预测敌方无人机的位置。为充分考虑“敌对障碍”约束,设计了一种混合自适应避障方法——改进动态窗避障PRM算法(dynamic window PRM, DW-PRM),以缩短规划路径。基于所提出的策略集和决策树,提出了突防策略。为提高动态避障能力,采用转弯半径约束求解多耦合突防同伦轨迹。仿真结果表明,提出的多约束条件下的突防同伦框架可以解决多无人机PMP问题。
Abstract
This paper examines a trajectory homotopy optimization framework for multiple unmanned aerial vehicles (multi-UAV) to solve the problem of dynamic penetration mission planning (PMP) with hostile obstacles and perception constraints. Constrained PMP problems are usually more challenging and difficult to solve with some practical constraints and requirements. To improve the efficiency of the solution for the penetration path, a novel variable-time mechanism has been constructed to adapt to the updated delay time of unknown target search (UTS) and dynamic trajectory planning (DTP) two stages. The occupancy grid maps are established by a Gaussian probability field (GPF) for predicting the positions of enemy UAVs. To fully consider the hostile obstacle constraint, a hybrid adaptive obstacle avoidance approach dynamic window PRM (DW-PRM) is designed to shorten the planned path. The penetration strategy algorithm (SG) is developed based on the proposed strategy set and decision tree. To improve the ability of dynamic obstacle avoidance, the multiple coupled penetration homotopy trajectory is addressed with a turning radius constraint. The simulation results indicated that the penetration homotopy framework for multi-constraints can solve the multi-UAV PMP problem.